Share This Article
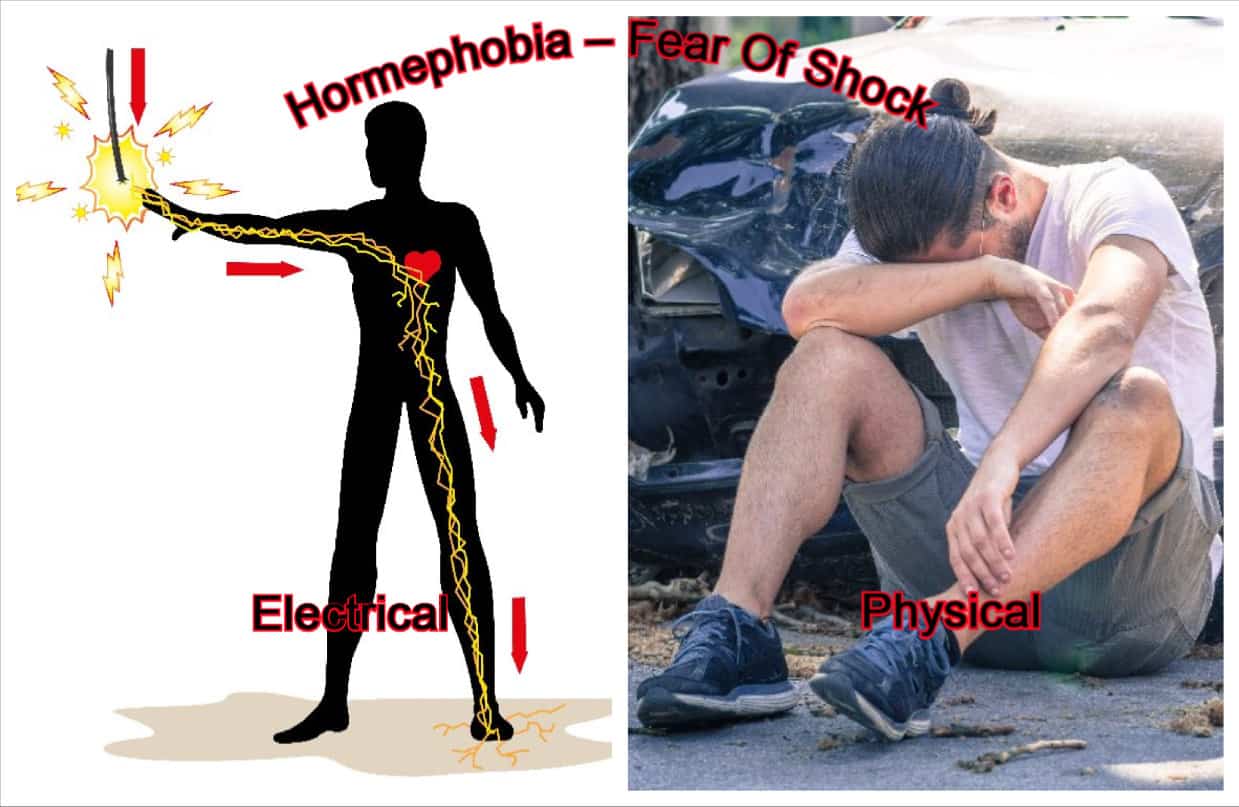
Hormephobia: A Shocking Issue
Do you enter a state of denial whenever you hear bad news? Do you go out of your way to avoid hearing it? Or, do you perhaps obsess over a fear of being electrocuted? If you answer the questions with a yes, you may have hormephobia, the fear of shock.
Shock can be physical or emotional.
Hormephobia is a fear of shock, which includes fear of emotional shock, fear of electrocution, and fear of electric shock. You probably find it hard to explain to your loved ones the stark terror that grips you when you are near an electric device or why the lightning in the sky makes you hide in your room.
However, you’re not alone. Many people have one type of phobia or the other. You can take a look at the complete list of phobias to know more about the types of phobias.
If you have a fear of shock, there is help. But the first step is educating yourself on your fear. Keep reading to learn more about hormephobia symptoms, hormephobia causes and treatment, and more.
What Is Hormephobia
Hormephobia is defined as the morbid fear of shock, either emotional or by electricity. A person with hormephobia will avoid any situation that makes them vulnerable to shock. The person will go to extreme lengths to avoid getting shocked, whether in response to bad news or by electricity.
These individuals are trying to avoid trauma. Many go into a state of denial due to emotional shock. Similarly, when it comes to fear of electricity, some avoid altogether electrical appliances or wiring.
The fear can reach a level where the patient starts experiencing panic attacks. It is at this stage that their daily activities become limited. The person may not leave their house for fear of meeting people who may deliver bad news. They close themselves off from people and possibly even appliances, living a minimalist life. This affects their social and work life, stripping them of their happiness and peace of mind.
Initially, this social avoidance may look like the key they’ve been searching for. However, with time, they may get used to this isolation and may even develop other mental illnesses, which can be detrimental. Early diagnosis and consistent treatment are necessary to treat specific phobias like hormephobia.
Hormephobia Causes
Like all other phobias, the exact cause of the fear is unknown. However, a multitude of factors could contribute to the development of the fear. Some reasons why a person may develop this irrational fear of shock are:
Genetic Predisposition
When a person has a family history of a psychiatric illness or any type of anxiety disorder, the probability of acquiring hormephobia increases considerably.
However, the person will only develop hormephobia if they are exposed to situations that make them fearful of shock.
Experiences
If someone had an experience of being electrocuted or has seen someone else being electrocuted, the fight-or-flight response kicks in and the person starts fleeing from any situation that may cause shock. This eventually develops into a phobia of shock.
When a person fears emotional shock, the phobia may stem from past incidents, including receiving bad news via calls or in person, which led to trauma whether physical or mental. This may cause them to avoid revisiting this feeling at all costs.
There have been instances where people have gone into a state of unconsciousness after receiving a shock. Depending on the severity and length of the shock, the individual may have mental as well as physical injuries, which serve as reminders of the incident.
Someone who has suffered an electric shock can have burns or some other visible mark on the skin that reminds them of the shock. Also, some people have become averse to even touching a switchboard after receiving a shock.
Knowing Someone Close
Hormephobia may also result from seeing someone go through the phobia. The devastating symptoms one may have witnessed can make them fear going through the same.
Also, hearing the shocking news of someone dying after being electrocuted can instill a fear of shock.
Hormephobia Symptoms
Depending on the severity of the phobia, a person may face four or more of these symptoms:
Physical Symptoms
- Dizziness
- Vomiting
- Shortness of breath
- Hyperventilation
- Rise in blood pressure
- Sweating
- Hot or cold flashes
- Trembling
- Headache
- Muscle tension
Physiological Symptoms
- Fear of getting shocked
- Anxiety even when thinking about shock
- Withdrawing from everyone
- Fear of dying
- Sadness
- Anxiety, anger, hopelessness
Hormephobia Treatment
Like all other phobias, the treatment for hormephobia is not specific. Also, while most phobias are entirely irrational, the fear of getting shocked or electrocuted is real and poses a real threat. So, it is not only people who have hormephobia who experience a fear of shocks.
However, if a person’s day-to-day life is limited due to fear, they should address it and work toward managing their fear. Some commonly used methods for treating phobias are listed below.
Self-Help
It is often said that self-help is the best help, and there’s truth to that. Although the fear of shocks is not entirely irrational, individuals with hormephobia make it the center of their existence. They constantly think about shock or being shocked.
However, patients are often aware that they need not worry or exercise so much control. Through self-help, they can work at their own pace, stopping when things get overwhelming and resuming when they calm down.
Those with this phobia are well aware of the internal turmoil and the triggers that set off the debilitating symptoms. With self-help methods, a person is their own guide and helps themselves build healthy coping mechanisms.
Meditation
Meditation is a fantastic way to fight stress and anxiety. It calms the mind and helps people overcome the turmoil they are facing. Through meditation, the mind becomes less preoccupied with negative thoughts as it has other things—like the breath or a chant—to focus on.
Psychology Therapy
Psychological therapies offer non-intrusive ways to help people overcome mental illnesses. Some therapies used to treat hormephobia are listed below.
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT)
Therapists frequently employ CBT to treat anxiety disorders. It is based on the premise that our thoughts and perceptions impact our behavior. The therapist uses CBT to help patients replace negative thoughts with constructive ones since phobias are irrational interpretations of reality.
Exposure Therapy
In this therapy, the patient is gradually exposed to the object of their fear in the presence of a health professional and in a controlled environment. It progressively accustoms the person to the object of their fear, so they can live with it without getting anxious.
Medication
Medication is only prescribed in extreme cases when a person is experiencing severe anxiety and frequent panic attacks. The medical health professional may prescribe medication like beta-blockers, antidepressants, and tranquilizers to relieve the symptoms of panic attacks.
Learning to Cope with Hormephobia
Living with hormephobia limits a person. It may reach a point where their normal functioning is affected. So, timely diagnosis and treatment are important. A person with this phobia needs to talk to a trusted family member or friend and seek medical help if self-help doesn’t seem to work.
Many professionals offer proven therapies and techniques to help individuals overcome their fear of shock and lead a normal life.
Let’s Conclude
Living with a phobia can be harmful to health, social, and work life. It affects an individual’s day-to-day functioning and often renders one lonely and prone to other mental health issues.
However, with timely help, a person can overcome their fear of shock to a large extent and live a fulfilling life.